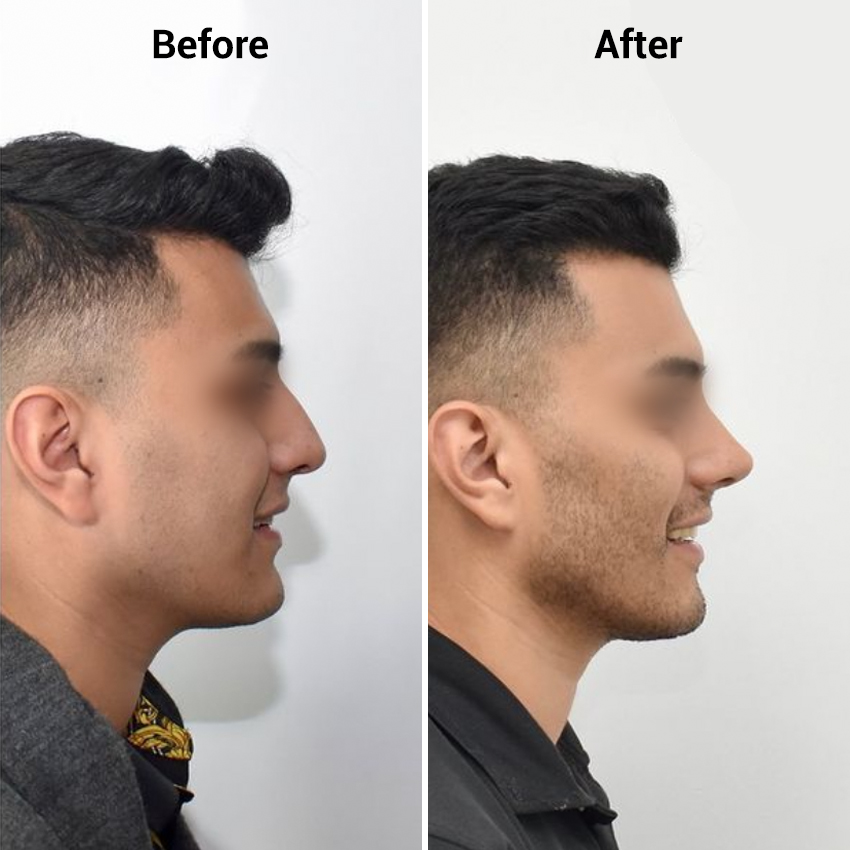
Rhinoplasty is a surgical procedure designed to reshape and enhance the nose’s appearance or function. It can be performed for cosmetic reasons or to correct structural issues that affect breathing.
This procedure can:
- Resize the nose (make it larger or smaller)
- Adjust the angle between the nose and upper lip
- Refine the nasal tip
- Correct bumps, indentations, or other irregularities
Rhinoplasty not only enhances facial harmony but can also improve nasal function for patients with breathing difficulties or structural deformities.
Rhinoplasty: A Transformative Procedure
Rhinoplasty, commonly known as nose reshaping surgery, serves both functional and aesthetic purposes. The procedure can:
- Enhance facial harmony by improving nose shape and size.
- Open blocked nasal passages caused by a deviated septum.
- Repair the deformity resulting after nasal fractures from injuries or trauma, left untreated or delayed or with poor outcome despite reduction treatment.
- Restore breathing function after disease, cancer treatments, or burns.
- Correct congenital abnormalities (birth defects).
How Rhinoplasty Reshapes the Nose
Rhinoplasty can address various nasal concerns, such as:
- Correcting a bulbous, upturned, hooked, or droopy nose.
- Fixing a deviated septum for better breathing.
- Reshaping nostrils that are too wide, small, large, or turned upward.
- Smoothing out noticeable bumps or dips on the nasal bridge.
- Adjusting the size of the nose to create a balanced facial appearance.
Surgical Approaches to Rhinoplasty
There are two primary techniques used in rhinoplasty:
Open Rhinoplasty – Recommended for major nasal reshaping, this method involves a small incision across the base of the nose (columella), allowing for full visibility and precise structural adjustments.
Closed Rhinoplasty – Suitable for minor corrections, this approach involves internal incisions within the nostrils, leaving no visible scars.
Types of Rhinoplasty:
Functional Rhinoplasty : Restores nasal form and function after disease, trauma, or previous medical treatments. It is also used to correct congenital defects and a deviated septum.
Secondary (Revision) Rhinoplasty : Performed to correct or refine results from a previous rhinoplasty. These procedures can range from minor touch-ups to complex structural repairs.
The Rhinoplasty Procedure: Step-by-Step
During rhinoplasty, the surgeon:
- Makes an incision inside the nostrils (closed rhinoplasty) or across the nasal base (open rhinoplasty).
- Lifts the nasal skin to access underlying bone and cartilage.
- Reshapes the nasal structure by reducing, adding, or repositioning bone and cartilage.
- Repositions the nasal skin to cover the newly shaped structure.
- Secures the skin with small sutures to ensure proper healing.
Recovery After Rhinoplasty
After surgery the patient has
- Internal Nasal Splint
- A soft silicone or plastic splint placed inside the nostrils.
- Supports the nasal structure and helps with breathing and healing.
- Often used if the septum is also operated on.
- Internal splints may be removed within 2-5 days.
- External Nasal Splint
- A firm plastic or aluminum splint or POP cast applied to the outside of the nose.
- Secured with tape or adhesive strips.
- Helps maintain the new nasal shape and protects the nose from accidental bumps.
- External splints are usually worn for 7-12 days.
- Nasal packing – Cotton gauze may be used inside the nose and is usually removed within 24 to 48 hours.
- Swelling and bruising – Common around the nose and eyes, gradually subsiding over a few weeks.
Patients is called on OPD basis for dressing change, suture removals, cast adjustment/removal and nasal cleaning from inside ( nasal toilet)
Rhinoplasty is a life-enhancing procedure that not only improves aesthetics but also restores proper nasal function. For expert rhinoplasty care, consult a trusted specialist to achieve the best possible results.

